The process of building a domestic wastewater treatment system designed by Nam Viet.
Domestic wastewater treatment is a very common need for most businesses. Domestic wastewater is considered a relatively easy type of wastewater to treat, however, to treat it effectively, we need to understand clearly. properties and understanding of processing technology.
Origin of wastewaterdomestic
- Water contained in human and animal waste such as feces, urine, blood, body fluids, toilet paper… is collectively called black wastewater
- Wastewater leaking from septic tanks and septic tank discharge pipes
- Wastewater generated from activities such as personal bathing, washing clothes, floor cleaning water, cooking wastewater… is often referred to as gray wastewater.
- Liquid waste remains in water sources such as: Cooking oil, drinking water, pesticides, lubricants, paint, cleaning chemicals…
Composition and properties of domestic wastewater
- Main ingredients: Organic matter, Nutrients of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), Sole solids badgers, Germs, disease-causing bacteria.
- Organic substances in wastewater (about 55-65%) will reduce the amount of dissolved oxygen in the water, affecting the life of aquatic animals and plants.
- Nutrients of N and P cause eutrophication of sources receiving wastewater, affecting living organisms in the aquatic environment.
- Suspended solids cause water turbidity, creating sediment deposits that clog drains, pipes and gutters.
- Organic substances in domestic wastewater are easily biodegradable.
- The content of decomposed organic matter is determined indirectly through the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) of wastewater.
Characteristics of domestic wastewater.
| STT | Target | Unit | Value |
| 01 | pH | – | 6 – 9 |
| 02 | BOD | mg/l | 220 |
| 03 | TSS | mg/l | 200 |
| 04 | Ammonium (NH4+) | mg/l | 80 |
| 05 | Nitrate (NO3-) | mg/l | – |
| 06 | Phosphate (PO43-) | mg/l | 9 |
| 07 | Animal and vegetable oils and fats | mg/l | 50 |
| 08 | Coliform | MPN/100ml | 1 ´ 107 |
Standards applicable to domestic wastewater QCVN 14:2008/BTNMT
| STT | Target | Unit | Value (QCVN 14 : 2008/BTNMT, Column A) | Value (QCVN 14 : 2008/BTNMT, Column B) |
| 01 | pH | – | 5 – 9 | 5 – 9 |
| 02 | BOD | mg/l | 30 | 50 |
| 03 | TSS | mg/l | 50 | 100 |
| 04 | Ammonium (NH4+) | mg/l | 5 | 10 |
| 05 | Nitrate (NO3-) | mg/l | 30 | 50 |
| 06 | Phosphate (PO43-) | mg/l | 6 | 10 |
| 07 | Animal and vegetable oils and fats | mg/l | 10 | 20 |
| 08 | Coliform | MPN/100ml | 3,000 | 5,000 |
Processes of Domestic Wastewater Treatment System
The wastewater treatment plan selected depends on the specific conditions of the Project and the treatment satisfies the following requirements:
- Does not make noise, does not cause unpleasant odors to the surrounding area.
- Does not affect the beauty and general activities of the resort and Spa
- Simple management and operation, reasonable operating costs.
From the above characteristics and the requirements to be achieved after treatment, wastewater treatment technology includes the following main steps:
- Step 1: Use mechanical methods to remove large substances suspended in water.
- Step 2: Use MBBR anoxic and aerobic biodegradation method to remove organic substances present in wastewater. Aims to reduce the amount of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and organic pollutant content in water (COD; BOD)
- Step 3: Use disinfection method to kill harmful microorganisms in water,
Ensure the output water meets discharge standards QCVN 14:2010/BTNMT Column Afor domestic wastewater
The sludge will be pumped to the sludge tank and periodically sucked.
Odors generated in the treatment tank cluster will be sucked into the odor treatment tank for treatment without causing odor to the area surrounding the system.
Domestic wastewater treatment technology diagram
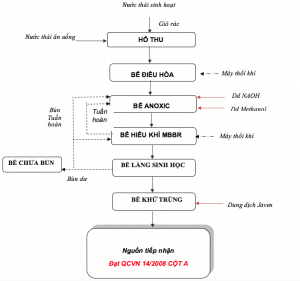
Diagram of domestic wastewater treatment technology
Some notes for domestic wastewater treatment systems
Clogged with garbage
- Domestic wastewater in Vietnam is characterized by the concentration of “everything in the world” from hair, cotton swabs, cigarette butts, shampoo packets, toothpicks, plastic straws…
li>
- Easy to clog the pile line, clog the pump, burn the pump, and when the pump fails, it overflows and cannot be treated
- Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to carefully removing trash before putting water into the treatment system to avoid unfortunate incidents such as pump fires, tank overflows, and untimely and ineffective treatment.
- Depending on the capacity of each factory, it is possible to design garbage screens, garbage collection baskets or garbage separators if necessary.
Fat congestion
- In companies that have canteens or kitchens for employees, the wastewater near the kitchen always has excess fat
- A large amount of grease that sticks for a long time can cause clogged pipes, clogged floats, and clogged pumps
- Reduces the efficiency of the main treatment system
- Therefore, it is necessary to remove grease before entering the main treatment system, and must be checked regularly.
- Depending on fat by flotation method, depending on the scale and amount of fat, it is possible to design a baffle ditch, a simple grease separator or a grease separator
Explanation of domestic wastewater treatment technology
Separate trash, separate grease, collect
- This wastewater flow, after passing through the local oil and grease separation system, will follow a large pipe through the sump.
- Before entering the wastewater collection pit, it must pass through a garbage separator with a gap of 2mm to avoid clogging the wastewater pump in the tank and protect the equipment for the unit’s construction behind it.
Garbage separation basket avoids clogging
- At the wastewater collection tank, it is pumped to the aeration tank by 02 submersible pumps operating alternately.
Air conditioning tank
- Wastewater in the regulation tank is regulated in flow and concentration.
- At the conditioning compartment, wastewater in the conditioning tank is transported by 02 submersible pumps that operate alternately to pump through the anoxic anoxic tank.

Install an Autocoupling submersible pump
Bể Anoxic
- In the Anoxic anoxic biological tank, the wastewater is mixed by a submersible agitator to create an anoxic environment for microorganisms to operate and best process Nitrate organic compounds.
- In addition, the anoxic biological tank is also supplemented with the nutrient chemical Methanol for microorganisms to use to increase treatment efficiency.
- At the anoxic tank, wastewater containing activated microbial sludge is circulated from the aerobic tank to ensure the best treatment time and environment.
- The Nitrification process occurs as follows: In an oxygen-deficient environment, these bacteria will reduce Nitrate Denitrificans will separate the oxygen of Nitrate (NO3) and Nitrite (NO2-) according to the metabolic chain:
NO3– → NO2– → N2O → N2↑
The molecular nitrogen gas N2 formed will escape the water and go outside.
- Wastewater from the Anoxic anoxic tank will flow gravity through the MBBR aerobic biological tank.
Aerobic biological tank
- In the MBBR aerobic biological tank, MBBR substrates help create an environment for aerobic microorganisms to adhere to increase the contact area of microorganisms with toxic organic substances in water, ammonium and nitrogen. total.
- In the MBBR Aerobic tank, wastewater is mixed with activated microbial sludge
- Air is supplied from 2 shallow air blowers that operate alternately 24/7 throughout the tank area
- Supply oxygen, create dissolved oxygen environment > 2mg/l is favorable for aerobic microorganisms to grow and decompose pollutants.
- Microorganisms will decompose organic substances into final products CO2 and H2O, reducing the concentration of dirt in wastewater.< /li>

Air blower – Fine air blower disc – MBBR tank
The MBBR aerobic biological tank is the unit that determines the treatment efficiency of the system because most of the pollutants in wastewater are organic substances that are easily biodegradable.
The process of treating biological aerobic MBBR wastewater includes the following stages:
Oxidation of organic substances:
CxHyOz + O2 (xt Enzyme)--> CO2 + H2O + ΔH
- Synthesis of new cells
CxHyOz + NH3 + O2 –> ; CO2 + H2O + C5H7NO2 + ΔH
Intracellular degradation:
C5H7NO2 + 5º2 (xt Enzyme)--> 5CO2 + H2O + NH3 ± ΔH
In addition, the group of autotrophic microorganisms Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter use nitrogen and phosphorus to metabolize nitrate and create biomass.
Nitrification occurs according to the following reaction equations:
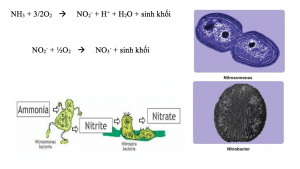
Bacteria participate in nitrogen metabolism
Phosphoritization process: Organic compounds containing phosphorus will be converted by Acinetobacter bacteria into new compounds that do not contain phosphorus and compounds that contain phosphorus but Easily decomposed by aerobic bacteria.
– Wastewater from the MBBR aerobic tank flows through gravity through the biological sedimentation tank.
At the biological sedimentation tank
- Water will be separated from mud.
- The microbial sludge will settle to the bottom and flow through gravity through the sludge compartment of the settling tank
- Then the sludge is pumped back to the anaerobic conditioning tank
- Excess sludge will be pumped to the sludge tank and periodically sucked by the functional unit.
- Water from the settling tank, after passing through the foam barrier and serrated trough, will flow by gravity to the disinfection tank.
At the disinfection tank
- Javen disinfectant chemicals will be injected to kill harmful microorganisms.
- After the water is disinfected, it will flow by gravity into the intermediate tank.
- The discharged water meets column A, QCVN 14:2008/BTNMT
Advantages of domestic wastewater treatment technology applied by Nam Viet
- Biological treatment process: is the process of treating nitrogen, phosphorus, and synthetic organic matter. In particular, the processes of nitrification and denitrification occur continuously in biological tanks. The denitrification process uses existing hydrocarbon sources in wastewater, does not require additional external hydrocarbon sources, limits the growth of filamentous bacteria and reduces caking and difficulty settling in the tank. sedimentation because it does not use settling tanks like traditional technologies.
- The Nitrate reduction process occurs, raising the pH and alkalinity of the wastewater, creating oxygen to facilitate the subsequent nitrification process, reducing the amount of gas needed for the nitrogen treatment process;
- Aerobic tanks have a high density of microorganisms per unit volume, so the organic load is high, thus the efficiency of organic matter treatment is higher and the ability to withstand shock loading is high. At the same time, due to the high density of microorganisms, the possibility of sludge generation is low
- Biotechnology minimizes investment costs for treatment systems, saving investment costs.
- The system’s operating process is controlled completely automatically, which eases operational work, saves electricity costs, and ensures that post-treated water quality is always stable and satisfactory.
Nam Viet always chooses effective solutions to optimize construction costs, reduce operating costs for customers, and ensure the system’s aesthetics. American and meets output standards. If you need advice or a survey for a quote, please contact Hotline 0932 562 177
Refer to wastewater treatment systems designed by Nam Viet here

Related articles
UASB tank in wastewater treatment
Introducing the UASB tank UASB stands for Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket, roughly translated as reverse...
Wastewater treatment of carton paper packaging production
Origin of wastewater from carton packaging production Wastewater containing printing ink generated during the production...
Common Aerotank tank problems and how to fix them
Aerotank incidents during the operation of the WWTP often arise equipment problems such as pumps,...